Simple explanation of Alkanes
Alkane is the general term for all the chains of carbon that have only single bonds.
Topics covered on this page (Alkanes):
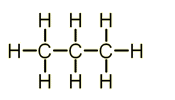
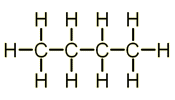
Structure of Alkanes
Structure of Alkanes
Structure of Alkanes
Alkanes are a homologous series (series of organic compounds that have the same general formula) of compounds have the general formula: CnH2n+2.
Here are the molecular formulae and names of the first five alkanes in the series:
Here are the molecular formulae and names of the first five alkanes in the series:
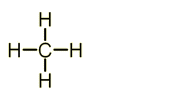
- Methane - CH4
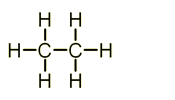
- Ethane - C2H6
- Propane - C3H8
- Butane - C4H10
- Pentane - C5H12
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons. This means that their carbon atoms are joined to each other by single bonds. This makes them relatively unreactive, apart from their reaction with oxygen in the air, which is called combustion, or burning.