Principles of chemistry.
2.1 understand the terms group and period
Groups are columns in the periodic table, the number of a group represents the number of electrons on an atom's outer shell.
Periods are rows on the periodic table, the row represents the number of orbitals that a atom has.
Periods are rows on the periodic table, the row represents the number of orbitals that a atom has.
2.2 recall the positions of metals and non-metals in the Periodic Table
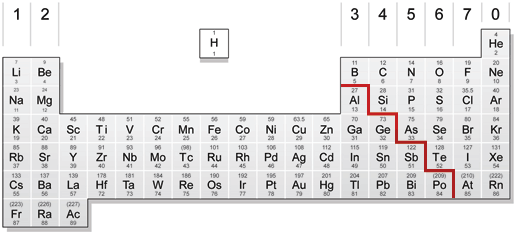
From left to right across a period there is a gradual change from metal to non-metal elements. For example, in Period 3, sodium, magnesium and aluminium are metals. They all conduct electricity and their oxides are basic. Phosphorus, sulphur, chlorine and argon are non-metals, They are all poor conductors of electricity and the oxides of P, S and Cl are acidic. Silicon has some properties of both a non-metal and a metal, so is therefore called a semi-metal or (metalloid). Silicon is a semi-conductor of electricity and is used in computer chips for this reason.
2.3 explain the classification of elements as metals or non-metals on the basis of their electrical conductivity and the acid-base character of their oxides
Metals are all conductors and they form metal-oxides, which are alkaline.
Nonmetals don't conduct and they form nonmetal-oxides, which are acidic.
If an element is electrically conductive and its oxide is basic, then it's a metal.
If an element is not electrically conductive and its oxide is acidic, then it's a non-metal.
Nonmetals don't conduct and they form nonmetal-oxides, which are acidic.
If an element is electrically conductive and its oxide is basic, then it's a metal.
If an element is not electrically conductive and its oxide is acidic, then it's a non-metal.
2.4 understand why elements in the same group of the Periodic Table have similar chemical properties
Elements that are in the same group of the periodic table have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons in their outer shell. The electrons in the outermost occupied shell (or shells) determine the chemical properties of the atom; it is called the valence shell.
Eg. Metals in the same group have the same number of electrons on their outer shell. This means they will behave in a similar way; they will react and bond similarly...
Eg. Metals in the same group have the same number of electrons on their outer shell. This means they will behave in a similar way; they will react and bond similarly...
- In group one the elements all form +1 ions as they each loose one electron to become stable (to have a full outer shell, they form this to become stable.)
2.5 understand that the noble gases (Group 0) are a family of inert gases and explain their lack of reactivity in terms of their electronic configurations.
Noble gasses do not react, they are inert (chemically unreactive.) They do not react because they have a full outer shell in each atom, which makes them stable. Having a full outer shell means that they do not need to gain, or loose electrons.
Group 0 (sometimes called Group 8) are called the Noble Gases, they are inert. These elements do not form compounds with other elements (most of the time). Helium is inert and is therefore a noble gas, however it is not always placed in Group 0. The reason for the lack of reactivity is the number of electrons in the outer shell of each atom. Helium and neon atoms have full outer shells, and the rest have 8 electrons in their outer shells. None of the atoms either gains or loses electrons easily.
Group 0 (sometimes called Group 8) are called the Noble Gases, they are inert. These elements do not form compounds with other elements (most of the time). Helium is inert and is therefore a noble gas, however it is not always placed in Group 0. The reason for the lack of reactivity is the number of electrons in the outer shell of each atom. Helium and neon atoms have full outer shells, and the rest have 8 electrons in their outer shells. None of the atoms either gains or loses electrons easily.
Here are some exam practice questions relating to the topic above.
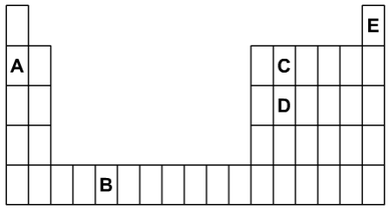
a) Which letters shown on the diagram are:
(i) Two elements in the same group?
(1 mark)
(ii) Two elements in the same period?
(1 mark)
(iii) Two elements that are metals?
(1 mark)
(iv) An unreactive gas?
(1 mark)
(Marks available: 4)
2. Sodium oxide forms an alkaline solution when it dissolves in water, sulphur dioxide forms an acidic solution.
a) What type of elements usually have alkaline oxides?
(1 mark)
b) What type of element usually forms acidic oxides?
(1 mark)
(Marks available: 2)
3. Elements of the periodic table that have similar properties are organised in to groups.
The following questions are about Group VII.
a) What name do we give to the Group VII elements?
(1 mark)
b) How many electrons do the members of Group VII have in their outer shell?
(1 mark)
c) What happens to the reactivity of the halogens as you go down Group VII?
Explain your answer.
(2 marks)
(Marks available: 4)
4. Transition metals are found in the centre section of the periodic table.
a) Give two ways that transition metals are different to Group I metals?
(2 marks)
b) Give one way that transition metal compounds are different to Group I metal compounds.
(1 mark)
(Marks available: 3)
The Periodic Table (Answers)
Answer outline and marking scheme for question: 1
a)
(i) C and D.
(1 mark)
(ii) A and C.
(1 mark)
(iii) A and B.
(1 mark)
(iv) E.
(1 mark)
(Total = 4 marks)
Answer outline and marking scheme for question: 2
a) Metals.
(1 mark)
b) Non-metals
(1 mark)
(Total = 2 marks)
Answer outline and marking scheme for question: 3
a) Halogens.
(1 mark)
b) 7.
(1 mark)
c) It decreases,
(1 mark)
because the atoms of the halogens are getting larger as you go down the group so they are do not gain
electrons as readily.
(1 mark)
(Total = 4 marks)
(Nucleus of elements lower down does not attract electrons as much as the higher elements as the positive
charge is shielded by the inner electrons).
Answer outline and marking scheme for question: 4
a) Any two from:
Transition metals are denser than water.
Transition metals have much higher melting/boiling points.
Transition metals do not react as vigorously.
Transition metals can be used as catalysts.
Or opposite statement referring to Group I metals.
(1 mark each, maximum 2 marks)
b) Either answer = one mark:
Transition metal compounds can be coloured, (Group I metals are white/colourless in solution).
Transition metals can form compounds with more than one formula.
Or opposite statement referring to Group I metals.
(1 mark)
(Total = 3 marks)
(i) Two elements in the same group?
(1 mark)
(ii) Two elements in the same period?
(1 mark)
(iii) Two elements that are metals?
(1 mark)
(iv) An unreactive gas?
(1 mark)
(Marks available: 4)
2. Sodium oxide forms an alkaline solution when it dissolves in water, sulphur dioxide forms an acidic solution.
a) What type of elements usually have alkaline oxides?
(1 mark)
b) What type of element usually forms acidic oxides?
(1 mark)
(Marks available: 2)
3. Elements of the periodic table that have similar properties are organised in to groups.
The following questions are about Group VII.
a) What name do we give to the Group VII elements?
(1 mark)
b) How many electrons do the members of Group VII have in their outer shell?
(1 mark)
c) What happens to the reactivity of the halogens as you go down Group VII?
Explain your answer.
(2 marks)
(Marks available: 4)
4. Transition metals are found in the centre section of the periodic table.
a) Give two ways that transition metals are different to Group I metals?
(2 marks)
b) Give one way that transition metal compounds are different to Group I metal compounds.
(1 mark)
(Marks available: 3)
The Periodic Table (Answers)
Answer outline and marking scheme for question: 1
a)
(i) C and D.
(1 mark)
(ii) A and C.
(1 mark)
(iii) A and B.
(1 mark)
(iv) E.
(1 mark)
(Total = 4 marks)
Answer outline and marking scheme for question: 2
a) Metals.
(1 mark)
b) Non-metals
(1 mark)
(Total = 2 marks)
Answer outline and marking scheme for question: 3
a) Halogens.
(1 mark)
b) 7.
(1 mark)
c) It decreases,
(1 mark)
because the atoms of the halogens are getting larger as you go down the group so they are do not gain
electrons as readily.
(1 mark)
(Total = 4 marks)
(Nucleus of elements lower down does not attract electrons as much as the higher elements as the positive
charge is shielded by the inner electrons).
Answer outline and marking scheme for question: 4
a) Any two from:
Transition metals are denser than water.
Transition metals have much higher melting/boiling points.
Transition metals do not react as vigorously.
Transition metals can be used as catalysts.
Or opposite statement referring to Group I metals.
(1 mark each, maximum 2 marks)
b) Either answer = one mark:
Transition metal compounds can be coloured, (Group I metals are white/colourless in solution).
Transition metals can form compounds with more than one formula.
Or opposite statement referring to Group I metals.
(1 mark)
(Total = 3 marks)
1. The outline below is of part of the periodic table. The letters shown represent some of the elements but they are
not the symbols of those elements.
not the symbols of those elements.