|
|
Sound
Sound waves are longitudinal waves that must pass through a medium. Sound is formed by things vibrating. Echoes are reflections of sounds. Their vibrations occur in the same direction as the direction of travel. Sound waves can only travel through a solid, liquid or gas. They can be reflected, refracted and diffracted.
Sound can't pass through a vacuum, as it requires atoms to pass on the energy.
Sound can't pass through a vacuum, as it requires atoms to pass on the energy.
The Speed of Sound
The speed of sound is dependent on the material that the sound is going through. It moves faster in a solid than a liquid or a gas because the molecules are closer together, and therefore can pass on the energy quicker.
The speed of sound in various materials:
The speed of sound in various materials:
- Air (at 0°C): 330 m/s
- Water: 1400 m/s
- Concrete: 5000 m/s
Vibrations
When an object or substance vibrates, it produces sound:
- the greater the amplitude, the louder the sound
- the greater the frequency, the higher the pitch.
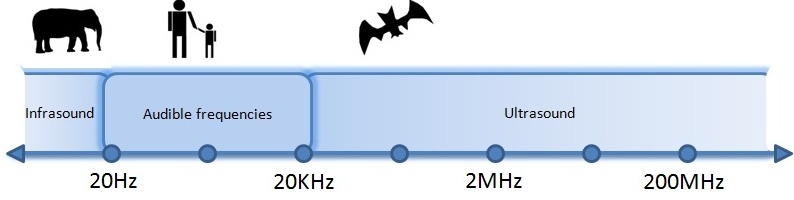
Human hearing range
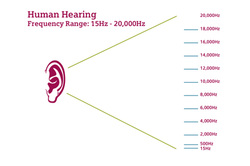
The normal range of human hearing is between around 20 Hz to 20 kHz, but the range becomes less as we get older. Sounds with frequencies above about 20 kHz are called ultrasound.
Three measurements of the Speed of Sound
1: Echoes
Method:
- Stand 50cm away from a wall
- When you clap, start a timer. When you hear the echoes, stop the timer.
2: Resonance Tube & Tuning Forks
Method:
- Fill up your resonance tube with water
- Strike tuning fork
- Using the water reservoir, lower the water surface. Listen for an increase in amplitude.
- When you find the loudest point, mark it with a rubber brand.