This page shows 9.1 - 9.10. Click on 'Geography' in the navigation menu bar to find another topic. - 999 I/GCSE Help
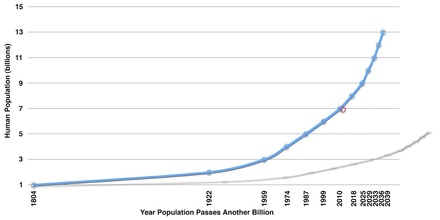
9.1 World population growth
The population of the world is growing at a rapid rate. In 2008, there were just over 6.7 billion people living in Earth. Now in 2013 there are over 7 billion people. This is a massive increase. All these people require food, water and shelter. They are all born with ambitions, and will want access to technology, education and opportunities.
Many people are worried that the world's population is growing too fast. People have feared that that the world could become overpopulated.
How and why is population changing in different parts of the world?
Many people are worried that the world's population is growing too fast. People have feared that that the world could become overpopulated.
How and why is population changing in different parts of the world?
|
Reasons for a HIGH BIRTH rate:
Reasons for a HIGH DEATH rate:
|
Reasons for a FALLING / LOW BIRTH rate:
|
9.2 Measuring population change
The population in countries are constantly changing. In some countries the population will be growing, and in some it may stay level, or decline. The difference in population is between the number of babies born and the number of people who die. This is called natural increase.
Birth Rate: The number of babies born in every 1000, in one year.
Death Rate: The number of people who die, for every 1000 people, in one year.
Natural Increase: The number of people added to, or lost from; the population for every 1000 people in one year.
Birth Rates and death rates vary between countries.
Factors than can affect differences between birth and death rates:
- The level of development of a country
- The religious views of the population in a country
- Policies of the Government
Birth Rate: The number of babies born in every 1000, in one year.
Death Rate: The number of people who die, for every 1000 people, in one year.
Natural Increase: The number of people added to, or lost from; the population for every 1000 people in one year.
Birth Rates and death rates vary between countries.
Factors than can affect differences between birth and death rates:
- The level of development of a country
- The religious views of the population in a country
- Policies of the Government
What are the advantages and disadvantages of having an ageing population?
Advantages:
- Larger proportion of ageing people can add experience to the workforce
- A growing 'grey' market for leisure and health products
- Cost of providing pensions, health care and sheltered housing leads to increased taxes on a proportionally small workforce
- Many young people are employed caring for the elderly. This harms a countries competitiveness, since they are not producing products for export.
9.3 Understanding how population changes over time
Advantages:
- Often in LEDCs children do not go to school and instead do work
- There are lots of potential workers in the future
- Young children need health care - for example, immunisations. This is expensive for a country to provide on a larger scale.
- Young people need to be educated - providing schools and teachers are expensive. Resources for lessons are difficult to access, and costly to buy.
- In the future, more children will reach bearing age, putting more pressure on health service. This will result in this cycle happening again in the future.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of having a youthful population?
9.4 Variations in population change
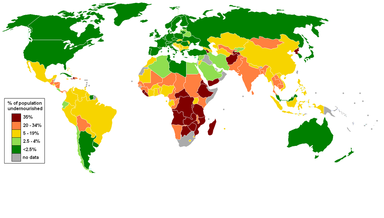
Although the population of the world is expected to grow till about 2200, the growth will not be even. The map to the left shows that :
-Population change is mainly happening in Africa, the Middle East, and parts of South America and South Asia
-Population balance is mainly found in North America and Europe
-Population change is happening in Russia and parts of Central and Eastern Europe.
It is important to understand that:
-Higher levels of population increases are occurring in developing (low income and middle income countries)
-Lower levels of population increase, population balance or even population decline mainly occur in developed countries.
Comparing two countries
Russia and Yemen
In 1950, the Russian population was 103 million. In Yemen there were just 4.3 million people. This meant that there were 24 Russians for every Yemeni.
In 2008, Russia's population had grown to 143 million and Yemen's population to 21 million.
By 2057, Russia's population is expected to fall to about 101 million, while Yemen's population is expected to rise to 105 million.
Russia's population will decline because of:
-Falling life expectancy for men, caused by industrial disease and alcoholism
-Outward migration of young men and women
-A low fertility rate of 1.2 children per woman
Yemen's population will grow quickly because of:
-Early age marriage
-Low literacy rates among women, meaning less Yemeni women will be finding jobs and instead marry.
-a high fertility rate of 6.7 children per woman, increasing life expectancy due to improved child vaccinations.
-Population change is mainly happening in Africa, the Middle East, and parts of South America and South Asia
-Population balance is mainly found in North America and Europe
-Population change is happening in Russia and parts of Central and Eastern Europe.
It is important to understand that:
-Higher levels of population increases are occurring in developing (low income and middle income countries)
-Lower levels of population increase, population balance or even population decline mainly occur in developed countries.
Comparing two countries
Russia and Yemen
In 1950, the Russian population was 103 million. In Yemen there were just 4.3 million people. This meant that there were 24 Russians for every Yemeni.
In 2008, Russia's population had grown to 143 million and Yemen's population to 21 million.
By 2057, Russia's population is expected to fall to about 101 million, while Yemen's population is expected to rise to 105 million.
Russia's population will decline because of:
-Falling life expectancy for men, caused by industrial disease and alcoholism
-Outward migration of young men and women
-A low fertility rate of 1.2 children per woman
Yemen's population will grow quickly because of:
-Early age marriage
-Low literacy rates among women, meaning less Yemeni women will be finding jobs and instead marry.
-a high fertility rate of 6.7 children per woman, increasing life expectancy due to improved child vaccinations.
9.5 Population change in Japan
Japan has the oldest population in the world:
- Over 65s make up 20.8% of the population
-The average age is 44 - the highest in the world
-The birth rate remains below replacement level (Meaning there is a decreasing population)
-Under 15's make up just 16.6% of the population
Japan has a very high ageing population, low working population and low youth population, meaning that the population is going to decrease; this is because women are marrying later on in lives, and men are getting low on sperm counts, and the older generation have got to live longer because of the medicines and cures available in Japan. The Japanese diet is one of the factors of the long life expectancy.
- Over 65s make up 20.8% of the population
-The average age is 44 - the highest in the world
-The birth rate remains below replacement level (Meaning there is a decreasing population)
-Under 15's make up just 16.6% of the population
Japan has a very high ageing population, low working population and low youth population, meaning that the population is going to decrease; this is because women are marrying later on in lives, and men are getting low on sperm counts, and the older generation have got to live longer because of the medicines and cures available in Japan. The Japanese diet is one of the factors of the long life expectancy.
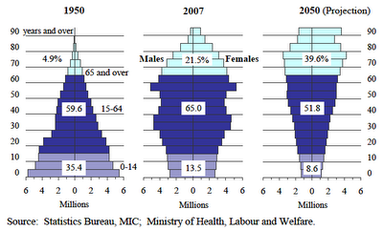
Why is Japan's population structure changing?
-People in Japan live longer. The average life expectancy is 79 for men and 85 for women. This is because of the healthy diets and good quality of life.
-Birth rate is declining because of the rise in the average age at which women have their first child.
-Japanese couples getting married has fallen, and the age at which people get married has risen, less likely to have a child at a young age as a consequence. This means it will take longer for babies to be born, thus worsening the Japanese problem.
What does this mean for Japan?
-An increase cost in pensions. More elderly people, living longer, will require pensions for longer.
-Fewer workers in the economy, so higher taxes needed to fund pensions.
-A rising number of elderly living in nursing homes.
-Increase in cost of healthcare, as more elderly people require medical treatment.
-People in Japan live longer. The average life expectancy is 79 for men and 85 for women. This is because of the healthy diets and good quality of life.
-Birth rate is declining because of the rise in the average age at which women have their first child.
-Japanese couples getting married has fallen, and the age at which people get married has risen, less likely to have a child at a young age as a consequence. This means it will take longer for babies to be born, thus worsening the Japanese problem.
What does this mean for Japan?
-An increase cost in pensions. More elderly people, living longer, will require pensions for longer.
-Fewer workers in the economy, so higher taxes needed to fund pensions.
-A rising number of elderly living in nursing homes.
-Increase in cost of healthcare, as more elderly people require medical treatment.
9.6 Population change in Mexico
What's happening to Mexico's population?
-Mexico has a large youthful population.
-Their population grew from just 20million in 1940 to 70million by 1980.
-The fertility rate in 1970 was as high as 7.1 but is much lower now. In 2008, it was still above the replacement level(2.1), at 2.4
-Mexico has a large youthful population.
-Their population grew from just 20million in 1940 to 70million by 1980.
-The fertility rate in 1970 was as high as 7.1 but is much lower now. In 2008, it was still above the replacement level(2.1), at 2.4
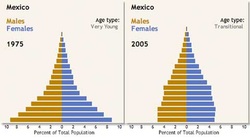
Why is Mexico's population changing?
- A low death rate
-Birth rate is falling
-Expected to take at least 50 years before the population structure of Mexico loses its Pyramid shape, and the population levels.
What does this mean for Mexico?
-A large youthful population requires an increase in school places.
-Large number of young people are unable to find work, so some migrate to the USA in order to find employment.
-There is a growing manufacturing industry to overtake the UK's and become the seventh largest economy in the world by 2050.
-Although Mexico is a strongly Catholic, abortion has been legalized in Mexico city in an attempt to reduce the number of abandoned children.
- A low death rate
-Birth rate is falling
-Expected to take at least 50 years before the population structure of Mexico loses its Pyramid shape, and the population levels.
What does this mean for Mexico?
-A large youthful population requires an increase in school places.
-Large number of young people are unable to find work, so some migrate to the USA in order to find employment.
-There is a growing manufacturing industry to overtake the UK's and become the seventh largest economy in the world by 2050.
-Although Mexico is a strongly Catholic, abortion has been legalized in Mexico city in an attempt to reduce the number of abandoned children.
9.7 Population policies around the world
China, introduced the one child policy because its population was getting extremely high, if it got too high then the population would be overflowed, meaning there wouldn't be enough resources for anyone. However, some families thought this policy was good, but for some it was bad news.
Pro-Natalist: The policy introduced to make women have children because of a low, decreasing population, meaning bad economic growth. Women would be paid to have children, forcing more women to have children, as some people would do anything to get their hands on money.
Anti Natalist Policy: Is a policy to reduce the population growth. They encourage people to have fewer children, as their population is getting too high and unstable.
Impacts of the one child policy:
-The policy has been successful in preventing 300 million births. However, it has some more negative effects.
-Some people now believe that China's rapidly growing economy will not have enough workers to keep it going. If this happens , the Chinese Government may be forced to relax the one-child policy.
-There is an imbalance of men to women. Couples have often used illegal methods to ensure that their one child is a boy, as boys are traditionally more able to care for their parents when they are elderly.
Pro-Natalist: The policy introduced to make women have children because of a low, decreasing population, meaning bad economic growth. Women would be paid to have children, forcing more women to have children, as some people would do anything to get their hands on money.
Anti Natalist Policy: Is a policy to reduce the population growth. They encourage people to have fewer children, as their population is getting too high and unstable.
Impacts of the one child policy:
-The policy has been successful in preventing 300 million births. However, it has some more negative effects.
-Some people now believe that China's rapidly growing economy will not have enough workers to keep it going. If this happens , the Chinese Government may be forced to relax the one-child policy.
-There is an imbalance of men to women. Couples have often used illegal methods to ensure that their one child is a boy, as boys are traditionally more able to care for their parents when they are elderly.
Here is a news excerpt portraying one of the major effects of the one child policy:
(Copyright CBC. Video licensed for noncommercial educational use on the 999GCSEHelp domain only.)
(Copyright CBC. Video licensed for noncommercial educational use on the 999GCSEHelp domain only.)
9.8 Making population policies work
Iran's Policy was:
Women are encouraged to wait 3-4 years between pregnancies and they are not allowed to have any children before they are 18 or if they are older than 35.
Families should be limited to 3 children and maternity leave benefits are restricted
Estonia's Policy was:
They introduced the 'mother's salary'.
Women are paid to have children
Working women receive 15 months' fully paid maternity leave, and non working women receive $200 per month
Women are encouraged to wait 3-4 years between pregnancies and they are not allowed to have any children before they are 18 or if they are older than 35.
Families should be limited to 3 children and maternity leave benefits are restricted
Estonia's Policy was:
They introduced the 'mother's salary'.
Women are paid to have children
Working women receive 15 months' fully paid maternity leave, and non working women receive $200 per month
Case Studies
ESTONIA (Pro-Natalist policy):
Problems of the policy:
CHINA (Anti-natalist policy):
Successes of the policy:
Problems of the policy:
ESTONIA (Pro-Natalist policy):
- In Estonia they were concerned that the population was going to half by 2050. Therefore they offered incentives to parents to have more children
- They introduced the 'mother's salary' - which effectively meant women were paid to have children. Working women were given 15 months maternity leave, while non-working women were given $200 a month.
- Birthrate has increased in Estonia
Problems of the policy:
- Fertility rate still remains below replacement level, thus meaning the population is still declining.
CHINA (Anti-natalist policy):
- The one-child policy, established in 1979, meant that each couple was allowed just one child. Benefits included increased access to education for all, plus childcare and healthcare offered to families that followed this rule.
Successes of the policy:
- Birth rate has fallen in China, thus reducing the speed of population growth in the country.
Problems of the policy:
- Many people claim that some women, who become pregnant after they had a child, were forced to have an abortion and many women were forcibly sterilised, sometimes without their consent (by their doctors). There appears to be evidence to back up these claims.
- Due to a traditional preference for boys, large numbers of female babies have ended up homeless or in orphanages, and in some cases killed. In 2000, it was reported that 90% of foetuses aborted in China were female. As a result, the gender balance of the Chinese population has become distorted. Today it is thought that men outnumber women by over 60 million. This will cause complications including trouble finding a partner.
9.9 Moving around
Migration in Russia:
Russia wanted all the migrants to come back to Russia, because their population was decreasing. They made policies persuading the migrants to come back, which was a huge success, as 6.5 million of those migrants came back to work in Russia.
UK:
Migrants move to the UK because we have better jobs, good housing, a good environment, good education, better standards of living from their country, where there might be war, lack of freedom and/or rights, natural disasters and racism and discrimination.
There are two main policies:
Open door:
Some countries have an open-door policy, where they let everyone into their country. This leads to high levels of immigration and thus bringing about some of the advantages and disadvantages seen in the table below.
Points-based:
Although you can migrate from within the European Union easily, it is far more difficult from the rest of the world. You instead need to go through a points-based system to come to work. Only migrants with specific skills are able to come and live in the UK – e.g. Scientists, teachers, nurses, construction workers etc. You need to get a visa and prove that you have the necessary skills to fill a skilled job. This means that you limit the amount of immigrants moving into your country, thus reducing some of the advantages and disadvantages seen in the table below:
Russia wanted all the migrants to come back to Russia, because their population was decreasing. They made policies persuading the migrants to come back, which was a huge success, as 6.5 million of those migrants came back to work in Russia.
UK:
Migrants move to the UK because we have better jobs, good housing, a good environment, good education, better standards of living from their country, where there might be war, lack of freedom and/or rights, natural disasters and racism and discrimination.
There are two main policies:
Open door:
Some countries have an open-door policy, where they let everyone into their country. This leads to high levels of immigration and thus bringing about some of the advantages and disadvantages seen in the table below.
Points-based:
Although you can migrate from within the European Union easily, it is far more difficult from the rest of the world. You instead need to go through a points-based system to come to work. Only migrants with specific skills are able to come and live in the UK – e.g. Scientists, teachers, nurses, construction workers etc. You need to get a visa and prove that you have the necessary skills to fill a skilled job. This means that you limit the amount of immigrants moving into your country, thus reducing some of the advantages and disadvantages seen in the table below:
9.10 Migration policy in USA
|
Advantages to the SOURCE country:
|
Disadvantages to the SOURCE country:
|
Please send an email to [email protected] or contact us on Twitter or Facebook if this is section (9.10) is not complete by 11 December
|
|
|