|
Studying development is about measuring how 'developed' one country is compared to other countries, or to the same country in the past.
Development measures how economically, socially, culturally or technologically advanced a country is. The two most common ways of measuring development are economic development and human development.
Indications of developmentRegions with high levels of development can be recognised by a high availability of medicines, health technology and educated workers.
There is no single way to calculate the level of development because of the variety of economies, cultures and peoples. Geographers use a series of development indicators to compare the development of one region against another. These indicators include:
|
|
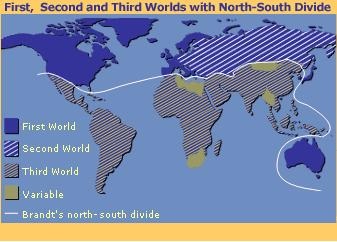
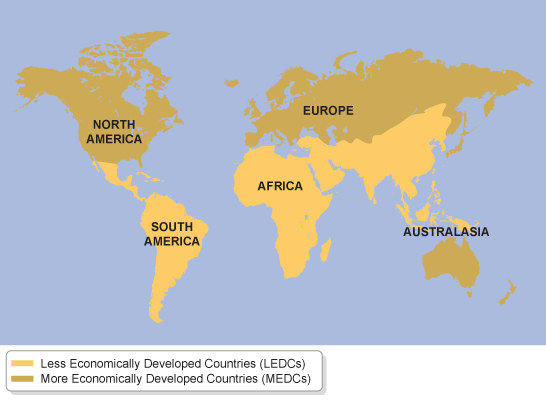
The 'Brandt Line' DivideMEDCs are countries which have a high standard of living and a large GDP. LEDCs are countries with a low standard of living and a much lower GDP.
The map shows the locations of LEDCs and MEDCs. Most of the southern hemisphere is less developed, while countries in the northern hemisphere are more developed. Development often takes place in an uneven way. A country may have a very high GDP - derived, for example, from the exploitation of rich oil reserves - while segments of the population live in poverty and lack access to basic education, health and decent housing.
Hence the importance of human development indicators, measuring the non-economic aspects of a country's development...
|
|
Measures of development
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is the most common measure of development.
GNI (Gross National Income) is also a commonly used measure of development.
HDI (Human Development index) is also a measure of development. Every country is given a number between 0 - 1. It measures:
Lastly, we'll look into the arguments for these 3 different measures: GDP, GNI and HDI.
GNI (Gross National Income) is also a commonly used measure of development.
HDI (Human Development index) is also a measure of development. Every country is given a number between 0 - 1. It measures:
- Life expectancy at birth
- Mean years of schooling
- Expected years of schooling
- Gross national income per capita.
Lastly, we'll look into the arguments for these 3 different measures: GDP, GNI and HDI.
Pros and Cons of GDP:
Positives (Pros) of GDP:
|
Negatives (Cons) of GDP:
|
Next, we'll look at Gross National Income (GNI).
Pros and Cons of GNI:
Positives / Pros of GNI:
|
Negatives / Cons of GNI:
|
Lastly, we'll analyse the Human Development Index (HDI).
Pros and Cons of HDI:
Positives (Pros) of HDI:
|
Negatives (Cons) of HDI:
|